DISEASE AND ILLNESS
Ngā māuiuitanga
Mpox
Mpox is a viral disease. It is not very contagious and is most commonly passed on through close physical or sexual contact. Cases have been identified in New Zealand but the risk of catching the virus remains low.
If you think you may have been exposed to mpox or if you develop symptoms, especially a rash, you should stay home and seek medical advice. You can contact your nearest sexual health clinic, your GP, or Healthline on 0800 611 116.
People at greater risk of mpox can be vaccinated for free. To check your eligibility and book an mpox vaccine appointment call Auckland Sexual Health on 0800 739 432. You can also contact your GP, or call Healthline on 0800 611 116.
Mpox symptoms can include a rash, spots or blisters. Some people also develop cold and flu symptoms, including a fever or swollen glands.
If you develop symptoms stay homeand seek medical advice. Many illnesses can cause similar symptoms so it may not be Mpox, but it’s important to get help.
Contact a sexual health clinic for free advice, call your GP, or ring Healthline for free anytime on 0800 611 116. 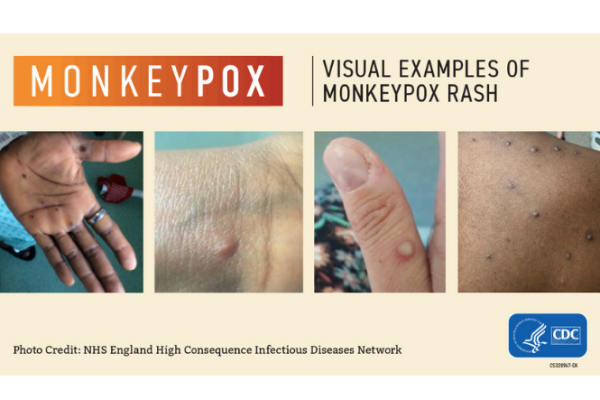
Mpox is a viral infection that is mainly spread through skin-to-skin contact with someone who has the virus.
It is not easily spread from person to person. The ways the virus can be passed on include:
- Close physical, intimate or sexual contact with someone who has mpox, via skin-to-skin contact
- Direct contact with the skin rashes, lesions, scabs or bodily fluids of someone with mpox
- Touching clothing, bedding or towels used by someone with a mpox rash
While rare, mpox can also be passed on through breathing in droplets exhaled by someone who has the virus. As this requires prolonged contact and for people to be very close together the risk of the virus spreading in this way is very low.
People are normally infectious and can pass on the virus from when they first develop symptoms, up until their lesions or scabs crust, dry and fall off. This will normally span around two to four weeks.
In countries where it is endemic (eg, Western Africa) animals sometimes harbour the virus and it can be passed on to humans through contact. When travelling to a country where mpox is endemic it’s important to avoid contact with animals, especially any that are sick or have been found dead.
While anyone can get mpox, the current global outbreak has mostly affected:
- men who have sex with men (MSM)
- people who have sex with MSM. This may include people of any gender or sexual identity, whether they are transgender or cisgender, and non-binary people.
Tests for mpox can be carried out at a medical practice or a sexual health clinic.
The test involves swabs of any lesions on your skin and/or a throat swab. The tests need to be carried out by a medical professional and cannot be done by a patient themselves.
It normally takes around 48 hours to get a result from the test. If the test shows you have Mpox, a public health professional will be in touch shortly after to provide further advice.
Mpox is a notifiable disease. This means that we will be told if someone tests positive for mpox.
This allows us to monitor the number of people who have the disease, and means we can give people with mpox advice on isolating, what to expect, and how to reduce the spread of the virus. We will also work with the case and sexual health services to identify and contact anyone else who may have been at risk of catching the virus. People with Mpox are contacted regularly by our team while isolating.
Guidance on what expect if you have Mpox is available from Health New Zealand (NZ) - Te Whatu Ora.
Last updated 17.10.2024
For health advice call Healthline for free anytime on 0800 611 116
Public
health topics
- Alcohol
-
Disease and illness
- Brucellosis (external site)
- Campylobacter
- Chikungunya
- Cholera
- COVID-19
- Cryptosporidium
- Dengue fever
- Foodborne and waterborne illness
- Gastroenteritis
- Giardia
- Haemophilus Influenza Type B
- Hand washing
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
- Hydatid disease (external site)
- Influenza (The Flu)
- Legionellosis (Legionnaires’ disease)
- Leptospirosis
- Listeria
- Malaria
- Measles
- Meningococcal disease
- Mpox
- Mumps
- Norovirus
- Paratyphoid fever (Enteric fever)
- Rheumatic fever
- Rickettsial disease (external site)
- Rotavirus
- RSV and other influenza like illnesses (ILI)
- Rubella
- Salmonella
- Shigellosis
- Tetanus
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Typhoid fever
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus gastroenteritis
- VTEC disease (STEC infection)
- Whooping cough (Pertussis)
- Yellow fever
- Yersiniosis
- Zika virus
- Early childhood education centre assessments
- Emergency planning and response
- Healthy environments
- Immunisation
- Smokefree environments
- Water
- Workplace health & wellbeing
- Are we the right agency?